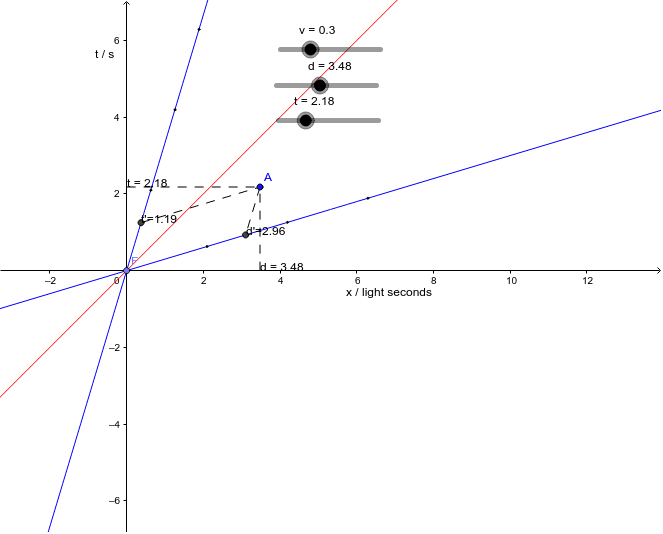
The space-time diagram above shows particles with different velocities. The horizontal value event is the position of the event as measured by observer 1.
Interactive Minkowski Diagram Spacetime Diagram
Gravity accelerates all objects equally.
. Sequence diagrams communication diagrams and timing diagrams. A powerful feature of digital video that we have exploited is the ability to combine parts of video images which occur at different times. If light cones are drawn in the positive and negative.
Use the sliders to adjust the speed of the other frame and the position of the dot in space-time. Particles 1 and 2 leave x 0 at t 0 accelerating from rest in opposite directions. And this site provides tutorials on software engineering tutorials programming language tutorials c programming tutorials operating system tutorials computer architecture and organization tutorials data structures tutorials dbms.
In this diagram which events out of A B C and D occur at the same time. Lines in the diagram are like contrails through time. One division of the space axis corresponds to 1 meter.
If one part of the video image contains the most interesting information we can select that section from each of several consecutive frames. An event a particular place at a particular time is represented by a point on the Minkowski Diagram. Now we want to show that the measurement of time intervals in the S frame are not the same as those in the S0frame using Minkowski diagrams.
The vertical value of this event is the time as measured by observer 1. Notice the two sets of equal angles. This sequence diagram tutorial is to help you understand sequence diagrams better.
Real-time control timing If the sample time of our program is T you can see that the program is executed at distinct points in. To explain everything you need to know from how to draw a sequence diagram to the common mistakes you should avoid when drawing one. This inertial frame sees another inertial frame S which.
I am trying to understand the basic conceptual ideas about the space-time diagrams. There are 3 types of Interaction diagrams. In such a diagram light rays always follow paths with a.
Hence a Flatland Minkowski Diagram is a 3-Space with light cones as in the diagram below. You can use the zoom slider to change the graphs scale. In Figure 7 we mark two events A and B located at the same point in space but different points in time in the.
A point on the spacetime diagram is called an event. An event is anything that can be characterized by a single point on a spacetime diagram or on a position vs time graph. Answer the following questions.
W e will not consider ho w space-time diagrams transform for t frames whic h is somewhat complicated and bey ond the scop e of curren t class. The Enterprise will fly by at a constant velocity past the planet and beam up the students without stopping. A space-time diagram shows the history of objects moving through space usually in just one dimension.
Home Grid Other Grid This shows the graph of how the coordinate axes change due to Lorentz transformations. Ct x light cone absolute future absolute. Create Space Time Cube By Aggregating Points Create.
Computation of each step within the sample time ie. Each such observer labels events in space-time by four inertial. The star goes supernova at space-time point S.
Creating a space-time cube allows you to visualize and analyze your spatiotemporal data in the form of time-series analysis integrated spatial and temporal pattern analysis and powerful 2D and 3D visualization techniques. Time axis is con v erted to distance b y m ultiply c. In a Flatland Minkowski Diagram there are two axes for space a plane and one axis for time.
Ct x x 45º 45º 12 v c v ct2 ct1 ct T142 Thect9- and x9-axes drawn on our ct-xspacetime diagram. This fact was known to Newton and tested to an accuracy of 1 part in 100 million by Eotvos. There are three tools that create a space-time cube for analysis.
One in which an observer is at rest relative to certain events and another for an observer in relative motion to the first. The space-time diagram above shows a proton and an antiproton moving under the influence of an electric field on the left and a gravitational field on the right. A speci c point on a space-time diagram is called an event To make a space-time diagram take many snapshots of the objects over time and set them on top of each other.
The two events will then appear in space and time given time unit 1 second. As already explained in our introduction the special theory of relativity describes the relationship between physical observations made by different inertial or nonaccelarating observers in the absence of gravity. Construct a world line of the particle that is resting at 2 m from the reference event.
This diagram is for a particular frame S and the space-time diagrams all other frames will be di eren t. Diagram for showing time dilation for events located at a fixed point in frame S. In spacetime diagrams we have events which are labeled as points on the diagram.
Another dot for event 2 because x 2x 1. Let us call we have an event on point A00and another event on B40 measured by an inertial frame S. Take a line from the event parallel to the space axis of observer 2.
Below the animation is a more detailed tutorial and some examples and excercises. Before the next step starts. An introduction to spacetime diagrams which are a valuable tool used to understand special relativity.
Please see the diagram below. T141 A spacetime diagram showing worldlines of three light pulses and three particles. A spacetime diagram or Minkowski diagram is a combination of two coordinate systems.
The second in a series on special and general relativ. The concept of space time diagram in pipelining is explained in this videoif you like the video then do sharethank you. Supernova spreads out in both directions along the trajectories shown.
Which events occur at the same place. The two events may also be shown in real time by pressing the buttons Play worldline t or Play worldline t. On the space-time diagram.
Minkowski space time diagram Minkowski space time diagram. This is a point in space at a speci c moment in time. Because the speed of light is special in relativity space-time diagrams are often drawn in units of seconds and light-seconds or years and light-years so a unit slope 45 degree angle corresponds to.
In the jargon of spacetime diagrams the green point on Toms and Sarahs plots is an event and the red or blue trajectories are worldlines. An event must have both a time and a place and. Assume that the planet is not moving relative to the star.
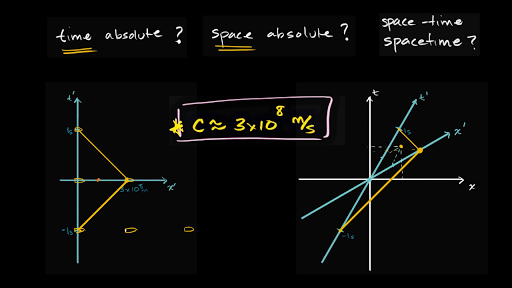
Introduction To Special Relativity And Minkowski Spacetime Diagrams Video Khan Academy

How To Really Draw Yourself Space Time Diagrams
Interactive Minkowski Diagram Spacetime Diagram
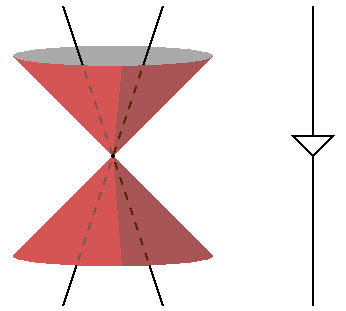


0 comments
Post a Comment